Last modification
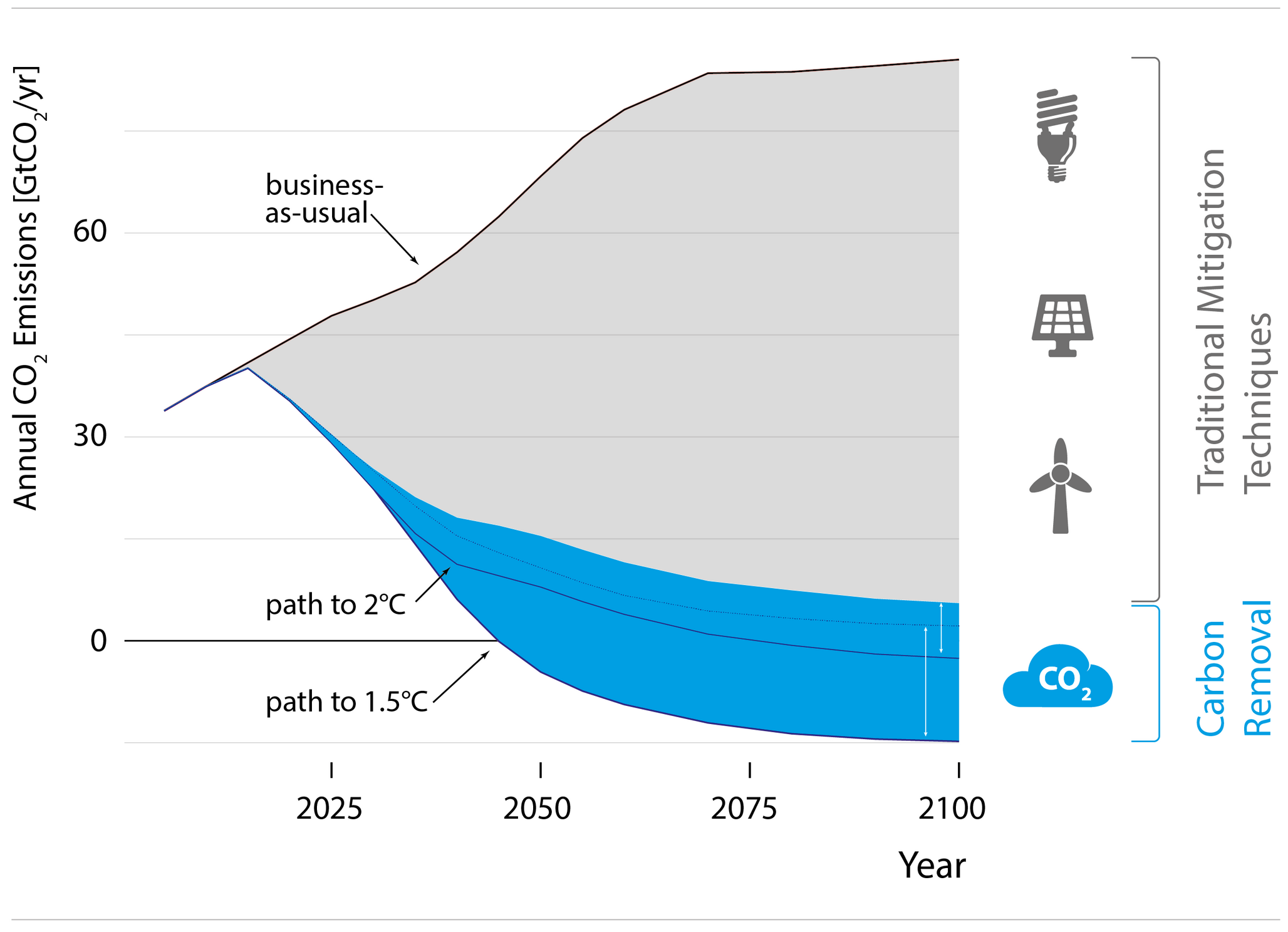
What are "negative emissions"?
Some examples of biological CDR, also known as natural sinks or nature-based solutions (NbS), include:
- Afforestation, i.e. large-scale planting of trees, and sustainable forest management which store carbon in soil and biomass.
- Adapted land management to increase and permanently bind carbon from atmospheric CO₂ in the soil, for example by ploughing-under crop residues or intercrops.
- Pyrolysis of biomass to biochar, which can return CO2 to the soil in a stable form and supports important soil functions (water and nutrient retention, soil structure, improvement of microbiology). This approach currently has the best technology readiness level for permanent CO2 removal and currently delivers the most ‘permanent CDR credits’ for the voluntary market.
- Restoration of reefs and seagrass in shallow ocean areas to efficiently store carbon dioxide.
- Agroforestry is the planting of trees on agricultural land. The trees are placed in such a way that the arable and pasture land below can continue to be used for agriculture and the yield of the production system is increased.
More detailed information on Nature-based Solutions can be found in this FAQ.
Examples of technological CDR are:
- Direct capture of CO₂ from the atmosphere and long-term storage in geological reservoirs (Direct Air Capture with Carbon Storage, DACCS)
- Bioenergy utilisation in combination with carbon capture and storage, meaning burning biomass in power plants and immediately capturing the CO₂ underground (Bio-Energy with Carbon Capture and Storage, "BECCS"). This process combines biological and technological CDR.
Geochemical CDR includes measures such as:
- Accelerated rock weathering
- Regulation of marine alkalinity
Technological and geochemical processes for carbon dioxide capture, use and storage (CCUS) are presently being developed and tested. However, as for biological CDR projects, any adverse side effects for ecological and social sustainability and the differing permanence must be taken into account.
In this regard, the economic impact and financial feasibility must also be evaluated in order to avoid, for example, highly developed technical solutions blocking too much capital for more efficient solutions. Compared to technical approaches, nature-based solutions have a higher impact (in tonnes) per franc invested. myclimate sees a high potential and the tremendous cost-benefit ratio for nature-based processes, i.e. projects based on soil-based negative emissions, such as reforestation, soil management, and the restoration of coastal wetlands and peatlands. Instead of technical measures, nature-based solutions offer the potential for positive interactions with each other (e.g. agroforestry, soil carbon and biochar) and at the same time support the urgently needed transformation of our agricultural system. On the other hand, we also support innovation into technological and geochemical processes to capture carbon. These technologies need to be developed to complement other CDR approaches to achieve net zero emissions. The longer global climate action lags behind the targets, the higher the negative emissions need to be to meet our climate change goals.
Sources:
FOEN 2022. Negative Emission Technologies (NET): an indispensable pillar of climate policy (German)
EASAC 2018. Negative emission technologies: What role in meeting Paris Agreement targets? Policy report 35.
IPCC 2019. Special Report on Climate Change and Land.
Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC) 2016. Vorsicht beim Wetten auf Negative Emissionen. MCC-Kurzdossier Nr. 2.
Swiss Carbon Removal Platform 2023. Fragen und Antworten zur CO2-Entnahme und -Speicherung
Swiss Carbon Removal Platform 2023. CDR Swiss Policy White Paper
You can find further exciting information on the subject of climate change and climate protection in our climate booklet